Filter and Search¶
TreeList and TreeView controls support the data filtering and searching features, which allow you to locate nodes based on their values.
Column Filters (TreeList)¶
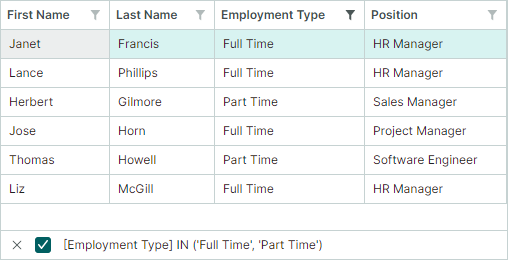
Users can filter TreeList columns using filter menus. To open a filter menu for a column, hover over the column header with the mouse until a filter button appears, and then click it. The opened filter menu contains all unique values from that column. Select an item in the filter menu to filter the column against this value.
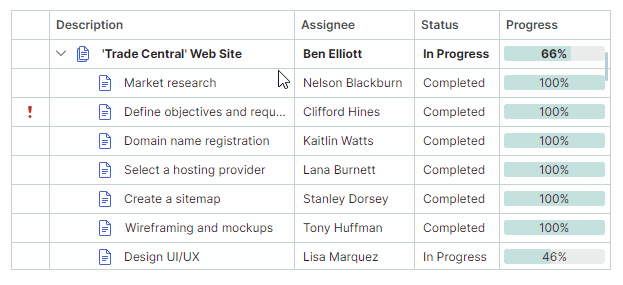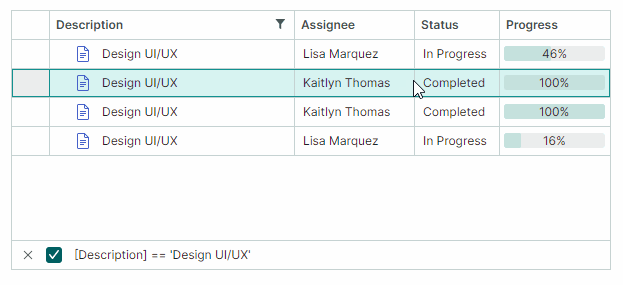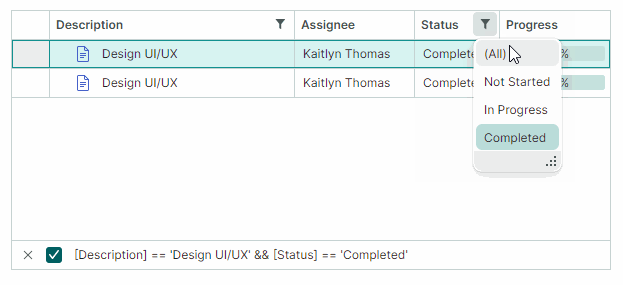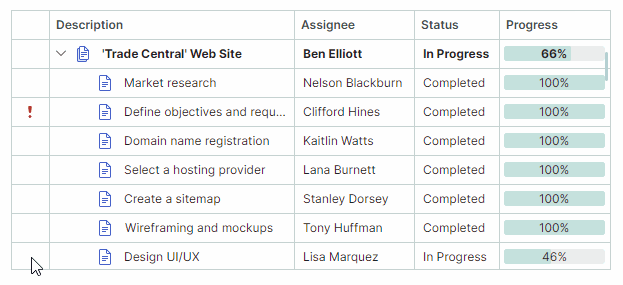
Users can filter the TreeList against multiple columns. Filters applied to multiple columns are combined by the AND operator.
'List' and 'Checked List' Display Modes¶
Filter menus can present items (column values) using one of two display modes:
-
List(default) — A regular list that allows a single item to be selected at a time.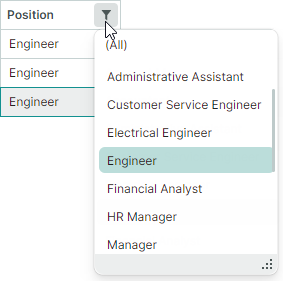
-
CheckedList— A list with checkboxes that allow users to select multiple items simultaneously.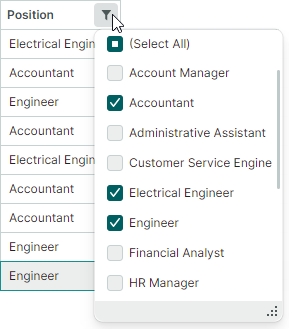
You can set filter menu display mode globally for all columns, or set it for individual columns, using the following properties:
-
TreeListControl.ColumnFilterPopupMode(default value isList) — Specifies default display mode for all column filter menus. This setting is applied to the columns that have theirTreeListColumn.FilterPopupModeproperty set tonull. -
TreeListColumn.FilterPopupMode(default value isnull) — Specifies filter menu display mode for individual columns. When set, this property overrides the global setting (TreeListControl.ColumnFilterPopupMode).
The following example applies CheckedList display mode to all columns, and List display mode to the City column.
treeList.ColumnFilterPopupMode = Eremex.AvaloniaUI.Controls.DataControl.FilterPopupMode.CheckedList;
treeList.Columns["City"].FilterPopupMode = Eremex.AvaloniaUI.Controls.DataControl.FilterPopupMode.List;
Filter Panel¶
Once a filter is applied, the filter panel appears at the bottom. It displays the currently applied filter criteria, and allows you to temporarily disable and clear the filter.
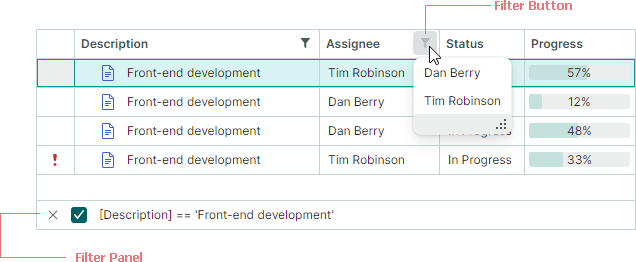
To learn how to filter programmatically, see the following section:
Related API¶
TreeList Control Members
-
AllowColumnFiltering— Gets or sets whether filter buttons are allowed for all columns. You can use a column'sColumnBase.AllowColumnFilteringproperty to override the global setting for individual columns.For instance, to disable filter buttons for all columns except one, set the
TreeListControl.AllowColumnFilteringproperty tofalse, and the target column'sColumnBase.AllowColumnFilteringproperty totrue. -
ColumnFilterButtonDisplayMode— Gets or sets whether filter buttons are always visible, or only appear when a user hovers a column header with the mouse (default). -
ColumnFilterPopupMode— Gets or sets default display mode (ListorCheckedList) for all column filter menus. Use a column'sFilterPopupModeproperty to override this setting for individual columns. -
CustomColumnDisplayTextevent — Allows you to provide custom display text for column values, including those in filter menus and the filter panel. When theCustomColumnDisplayTextevent fires for values in the filter panel, the event'sNodeparameter returnsnull. -
FilterPanelText— Gets the text representation of the filter displayed in the filter panel. -
FilterPanelDisplayMode— Gets or sets the filter panel's visibility mode. Available options include:Auto(default) — The filter panel appears when a filter is applied to any column.Never— The filter panel is always hidden.
-
FilterString— Gets or sets the filter criteria applied to the control. You can use this property to construct a filter in code. TheFilterStringproperty is supported by the TreeList and TreeView controls. -
IsFilterEnabled— Gets or sets whether the filter is active. TheIsFilterEnabledproperty is supported by the TreeList and TreeView controls. -
IsFilterPanelVisible— Gets whether the filter panel is currently visible.
Column Members
ColumnBase.AllowColumnFiltering— Gets or sets whether a filter button is allowed for the current column. To enable or disable filter buttons for all columns, see theTreeListControl.AllowColumnFilteringsetting. TheColumnBase.AllowColumnFilteringoption allows you to override theTreeListControl.AllowColumnFilteringsetting for individual columns.-
ColumnBase.ColumnFilterMode— Gets or sets how a column's data is filtered. Available options include:Value— A column's data is filtered by underlying values.DisplayText— A column's data is filtered by cell display text.
-
ColumnBase.FilterPopupMode— Gets or sets filter menu display mode (ListorCheckedList) for individual columns. When set, this property overrides the control'sColumnFilterPopupModeproperty. -
ColumnBase.IsFiltered— Gets whether a filter is applied to the current column. ColumnBase.RoundDateTimeForColumnFilter— Gets or sets whether to ignore the time portion of DateTime values when constructing filters for columns that display DateTime values. This property is in effect for filters created using column filter menus and the auto filter row.
Search Panel (TreeList and TreeView)¶
The Search Panel helps a user quickly locate rows by the data they contain. When a user types text in the Search Panel, the control displays those rows that contain the typed text.

- The search functionality is case-insensitive.
- The Contains comparison operator is used for data searching.
- Data search is performed across all columns in the TreeList control.
Set the control's SearchPanelDisplayMode property (inherited from the DataControlBase class) to one of the following values to enable the Search Panel:
SearchPanelDisplayMode.Always— The control permanently displays the Search Panel.SearchPanelDisplayMode.HotKey— The control displays the Search Panel when a user presses the CTRL+F hotkey. The ESC shortcut clears the Search Panel. A subsequent ESC key press closes the panel. A user can also activate the Search Panel from a column header's context menu.
The TreeListControlBase.FilterMode property specifies which nodes are displayed when matches found. Three filter modes are supported:
FilterMode.ShowMatches— Displays nodes that match the search text.FilterMode.ShowMatchesWithAncestors— Displays nodes that match the search text, and their parent nodes.FilterMode.ShowBranchesWithMatches— Displays entire branches if they contain nodes that match filter criteria.
Search in Collapsed Nodes¶
During data search/filtering, the TreeList/TreeView controls can search within collapsed nodes. Set the TreeListControlBase.ExpandNodesOnFiltering option to true to search in collapsed nodes and automatically expand them when a match is found.
The controls only search through currently loaded nodes. For hierarchical data sources, you can set the AllowDynamicDataLoading property to false to disable dynamic node loading and load all nodes at once.
Related API¶
DataControlBase.IsSearchPanelVisible— Gets whether the Search Panel is currently visible.DataControlBase.SearchPanelHighlightResults— Specifies whether to highlight the search text in the found nodes. The property's default value istrue.DataControlBase.SearchText— Gets or sets the search text. You can assign a value to this property to filter the control in code. This filtering functionality is supported even if the Search Panel is hidden or disabled (theSearchPanelDisplayModeproperty is set toSearchPanelDisplayMode.Never).DataControlBase.ShowSearchPanelCloseButton— Allows you to hide the Search Panel's built-in Close button.TreeListControlBase.ExpandNodesOnFiltering— Specifies whether to expand collapsed nodes during data searching/filtering when their child nodes match the current filter/search criteria.
Example¶
The following code makes the Search Panel always visible, and enables the display of filtered nodes along with their parents. The SearchText property is used to set the search text.
treeList.SearchPanelDisplayMode = SearchPanelDisplayMode.Always;
treeList.FilterMode = FilterMode.ShowMatchesWithAncestors;
treeList.SearchText = "department";
Auto Filter Row (TreeList)¶
The Auto Filter Row is a special row displayed above all TreeList nodes. It allows a user to type text in its cells to filter data against corresponding columns.

- The filter functionality is case-insensitive.
- To search in collapsed nodes and expand them when a match is found, set the
TreeListControlBase.ExpandNodesOnFilteringoption totrue. See also: Search in Collapsed Nodes. - The control's default filter mode is to only display nodes that match the specified criteria. Set the
TreeListControlBase.FilterModeproperty toFilterMode.ShowMatchesWithAncestorsto display target nodes along with their parents.
Enable Auto Filter Row¶
Set the TreeList.ShowAutoFilterRow property to true.
Enable Runtime Filter Operator Selectors¶
You can allow users to choose filter logic for Auto Filter Row cells at runtime. When this feature is active, a filter operator icon appears in each Auto Filter Row cell. Users can click this icon to open a dropdown menu and select the desired operator.
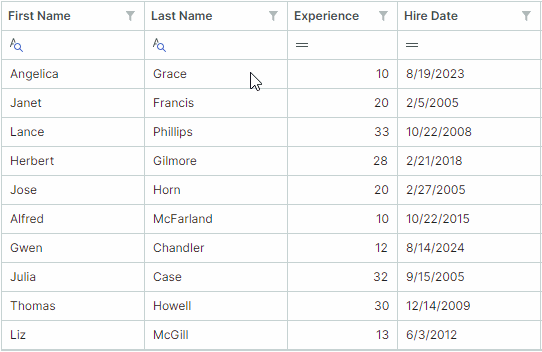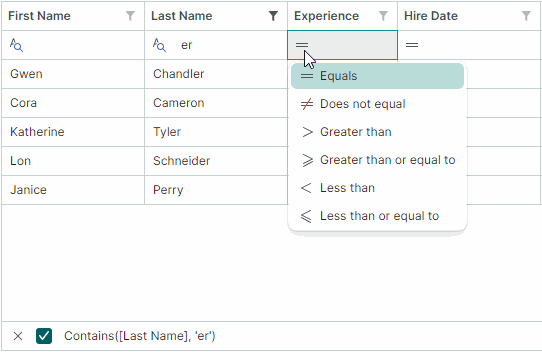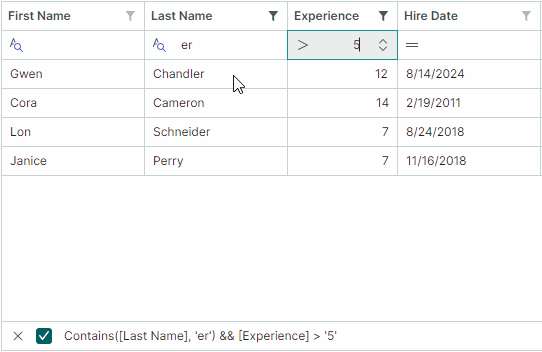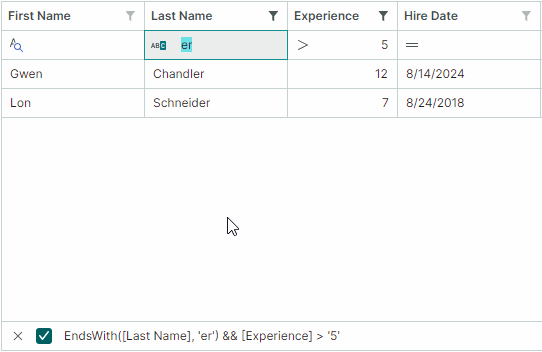
Use the following properties to enable filter operator selectors:
TreeListControl.ShowConditionInAutoFilterRow(default isfalse) — Specifies the default visibility of filter operator selectors for all Auto Filter Row cells (columns).ColumnBase.ShowConditionInAutoFilterRow— Enables or disables the filter operator selector for an individual column. This property overrides theTreeListControl.ShowConditionInAutoFilterRowsetting.
Specify Filter Operators in Code¶
Use the ColumnBase.AutoFilterCondition property to programmatically specify filter operators for individual Auto Filter Row cells (columns). The following filter operators are supported:
Contains(applicable to string values) — Row values must contain the entered text.-
Default— Default mode.Defaultis equivalent to theContainsoption for the String and Object data types.Defaultis equivalent to theEqualsoption for other data types.
-
DoesNotContain(applicable to string values) — Row values must not contain the entered text. DoesNotEqual— Row values in the target column must not match the entered value.EndsWith(applicable to string values) — Row values must end with the entered text.Equals— Row values must match the entered value.Greater— Row values must be greater than the entered value.GreaterOrEqual— Row values must be greater than or equal to the entered value.Less— Row values must be less than the entered value.LessOrEqual— Row values must be less than or equal to the entered value.StartsWith(applicable to string values) — Row values must start with the entered text.
Specify Filter Values¶
The ColumnBase.AutoFilterValue property allows you to set a value for a specific Auto Filter Row cell in code. You can use the ColumnBase.AutoFilterValue property to filter the TreeList even if the Auto Filter Row is hidden.
Example¶
The following code activates the Auto Filter Row and displays nodes whose values in the 'Name' column start with "M".
treeList1.ShowAutoFilterRow = true;
TreeListColumn colName = treeList1.Columns["Name"];
colName.AutoFilterCondition = AutoFilterCondition.StartsWith;
colName.AutoFilterValue = "M";
Filter Nodes Dynamically Using an Event¶
The CustomNodeFilter event allows you to hide specific nodes based on a custom condition. This event fires for each node in the following cases:
- The control's item source changes.
- The control's nodes are filtered (for instance, using the Search Panel and/or Auto Filter Row).
- The control's
RefreshDatamethod is called.
Use the Node event parameter to identify the currently processed node. To hide the node, set the Visible event parameter to false.
Example - Filter Rows with an Event¶
In the following example, a Tree List control displays a list of ProjectTask objects. The CustomNodeFilter event is handled to implement custom node filtration. Nodes are hidden according to a value of the ProjectTask.Status property.
It is assumed that the example contains the "Enable Filter" toggle button that activates and deactivates the custom filtration. When the button is clicked, the ToggleButton.IsCheckedChanged event handler calls the RefreshData method to refresh treelist nodes and re-raise the CustomNodeFilter event.
<ToggleButton Name="btnEnableFilter" Content="Enable Filter" IsCheckedChanged="BtnEnableFilter_IsCheckedChanged"/>
<mxtl:TreeListControl x:Name="treeList" CustomNodeFilter="TreeList_CustomNodeFilter">
<!-- ... -->
using Eremex.AvaloniaUI.Controls.TreeList;
private void BtnEnableFilter_IsCheckedChanged(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
treeList.RefreshData();
}
private void TreeList_CustomNodeFilter(object sender, TreeListCustomNodeFilterEventArgs e)
{
bool filterEnabled = btnEnableFilter.IsChecked == true;
if (!filterEnabled)
return;
ProjectTask task = e.Node.Content as ProjectTask;
e.Visible = task.Status!= DemoData.TaskStatus.Completed;
}
Filter in Code (TreeList and TreeView)¶
Starting with version 1.2, you can use the DataControlBase.FilterString property to programmatically filter data in the TreeList and TreeView controls.
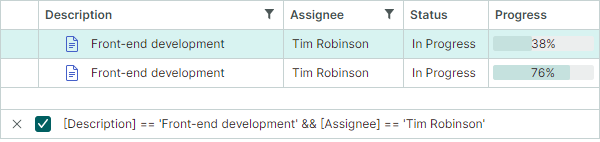
A filter string consists of individual filter expressions combined by logical operators (AND or OR).
Clear and Disable the Filter¶
- To clear the filter, set the
FilterStringproperty tonullor an empty string. - To temporarily disable the filter, use the
DataControlBase.IsFilterEnabledproperty.
Specify Columns¶
In the filter string, columns should be referenced by their field names enclosed in square brackets. Examples:
[FirstName][Position]
Specify Constants¶
-
Numeric constants must specified using standard numeric formats. Examples:
500,010.314,.512.0m/12.0M,12d/12D,12f/12F-32.5-
String constants must be wrapped in single quote characters (
'). To insert'as a literal, use the''notation. Examples: -
'Research and Development' 'Clair de lune''O''Neil'
-
DateTime and DateTimeOffset constants must be wrapped with the
#characters and specified using an invariant culture. Examples:#2018-03-22##2018-03-22 13:18:51##2018-03-22 13:18:51.94944#
-
DateOnly and TimeOnly constants must be enclosed between
#!and!#strings. Examples:#!2026-01-01!##!12:23:45!#
-
Boolean constants:
true,True, orTRUEfalse,False, orFALSE
Logical Operators¶
You can use the following logical operators to combine individual expressions in a filter string:
&&,and,AndorAND||,or,OrorOR
Operators and Functions¶
The following table lists available operators and functions to construct filter expressions:
| Operators and Functions | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
= or == |
Equal to | [Price] = 500 |
!= or <> |
Not equal to | [Price] != 500 |
< |
Less than | [Price] < 700 |
> |
Greater than | [Price] > 600 |
<= |
Less than or equal to | [Price] <= 600 |
>= |
Greater than or equal to | [Price] >= 800 |
is null |
Selects null values | [Region] is null |
is not null |
Selects non-null values | [Region] is not null |
IsNull |
Selects null values | IsNull([Region]) |
IsNullOrEmpty |
Selects null values and empty strings | IsNullOrEmpty([Region]) |
In |
Selects items that have any of the specified values. | [City] In ('Beijing', 'Shenzhen', 'Chengdu') |
Contains |
Selects items that contain the specified string. The Contains operator is case-insensitive. | Contains([Name], 'lan') |
StartsWith |
Selects items that start with the specified string. The StartsWith operator is case-insensitive. | StartsWith([Product], 'CPU') |
EndsWith |
Selects items that end with the specified string. The EndsWith operator is case-insensitive. | EndsWith([Product], '9950X') |
!, not, Not or NOT |
Negation operator | !Contains([Maker], 'amd') |
Advanced Filter Expressions¶
You can use the Eremex.AvaloniaUI.Controls.Data.Filtering.ExprStringBuilder class to create advanced filter criteria. These filter criteria can include operations on operands, calls of supported functions, and more. To construct filter criteria, use members of the ExprStringBuilder class.
To get a filter string, call the ToString method of a resulting ExprStringBuilder object. You can then assign this filter string to a target control's DataControlBase.FilterString property.
// [Price] * [Stock] > 5000m
// Note: All operands ([Price], [Stock] and '5000') must be of the same data type (e.g., decimal). Otherwise, the control will fail to evaluate the expression.
var filter = ExprStringBuilder.Property("Price").Multiply(ExprStringBuilder.Property("Stock")).GreaterThanValue(5000m);
var filterString = filter.ToString();
control.FilterString = filterString;
Important
Currently, expression operands (column data types and constants) must be of the same data type. Using different data types (e.g., decimal and integer) in the same expression is not currently supported.
// [PropertyA] IN (([PropertyB] + 2m) % 3.0, 'ABC', null)
var filterString = ExprStringBuilder.Property("PropertyA").In(ExprStringBuilder.Property("PropertyB").AddValue(2m) .ModuloValue(3d), ExprStringBuilder.Constant("ABC"), ExprStringBuilder.Null()).ToString();
control.FilterString = filterString;
Specify Enumeration Values¶
To specify enumeration values in a filter string, you should construct filter criteria using the Eremex.AvaloniaUI.Controls.Data.Filtering.ExprStringBuilder class.
The ExprStringBuilder.ToString method allows you to get a filter string, which you can assign to a target control's FilterString property.
You also need to register the enumeration type using the EnumProcessingHelper.RegisterEnum method before the filter string is assigned to the target control.
Examples - Use Enumeration Values in Filter Expressions¶
The following two examples create filter expressions against the EmploymentType column. This column displays EmploymentKind enumeration values.
public enum EmploymentKind
{
[Display(Name = "Full Time")]
FullTime,
[Display(Name = "Part Time")]
PartTime,
Contract
}
Example 1¶
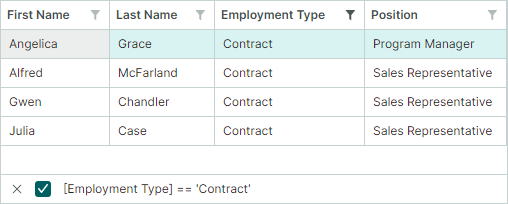
The expression below uses the ExprStringBuilder.EqualValue function to select rows where the EmploymentType column is equal to EmploymentKind.Contract.
Take note of the EnumProcessingHelper.RegisterEnum method used to register the EmploymentKind enumeration.
using Eremex.AvaloniaUI.Controls.Data.Filtering;
EnumProcessingHelper.RegisterEnum(typeof(EmploymentKind));
// [EmploymentType] = 'Contract'
var filterString1 = ExprStringBuilder.Property("EmploymentType").EqualValue(EmploymentKind.Contract).ToString();
control.FilterString = filterString1;
Example 2¶
The following expression uses the ExprStringBuilder.InValues function to generate the In operator. This expression checks whether the EmploymentType column is equal to EmploymentKind.FullTime or EmploymentKind.PartTime.
// [EmploymentType] IN ('FullTime', 'PartTime')
var filterString2 = ExprStringBuilder.Property("EmploymentType").InValues(EmploymentKind.FullTime, EmploymentKind.PartTime).ToString();
control.FilterString = filterString2;