Camera
A camera is a virtual representation of a viewpoint that defines how a 3D model is projected onto the 2D screen. The Graphics3DControl allows you to choose between an isometric and perspective camera, and manage the settings and position of the camera in code.
The default camera used by Graphics3DControl is perspective.
The Graphics3DControl.Camera property allows you to access the current camera object. However, initially this property returns null, which means that the Graphics3DControl uses the default camera (perspective).
To access and customize the camera object in code, you need to explicitly initialize the Graphics3DControl.Camera property with a PerspectiveCamera or IsometricCamera object.
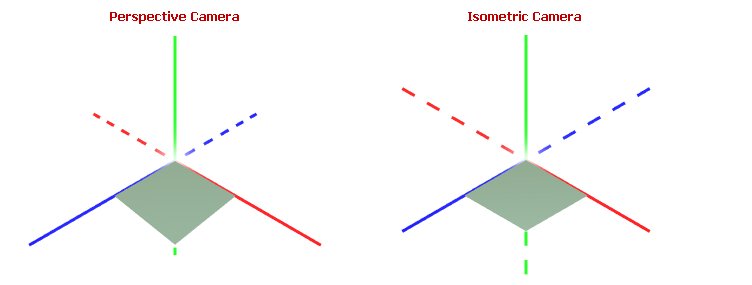
Perspective Camera
A perspective camera simulates realistic depth perception by projecting a 3D model onto a 2D plane, making objects appear smaller as they get farther away.
The perspective camera is default in the Graphics3DControl. To access the camera object and customize its settings, set the Graphics3DControl.Camera property to a PerspectiveCamera object.
xmlns:mx3d="https://schemas.eremexcontrols.net/avalonia/controls3d"
<mx3d:Graphics3DControl Name="g3DControl" ShowAxes="True">
<mx3d:Graphics3DControl.Camera>
<mx3d:PerspectiveCamera FieldOfView="0.9" />
</mx3d:Graphics3DControl.Camera>
</mx3d:Graphics3DControl>
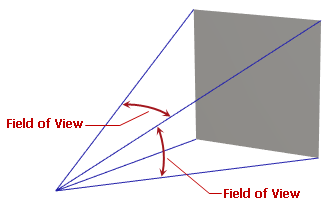
The PerspectiveCamera.FieldOfView property allows you to specify the field-of-view angle of the perspective camera, expressed in radians. The property's default value is MathF.PI/4.
Isometric Camera
An isometric camera maintains a consistent scale for all objects regardless of their distance from the camera.
Set the Graphics3DControl.Camera property to an IsometricCamera object to switch to an isometric camera.
xmlns:mx3d="https://schemas.eremexcontrols.net/avalonia/controls3d"
<mx3d:Graphics3DControl Name="g3DControl" ShowAxes="True">
<mx3d:Graphics3DControl.Camera>
<mx3d:IsometricCamera FarClipPlane="1000"/>
</mx3d:Graphics3DControl.Camera>
</mx3d:Graphics3DControl>
View Predefined Scenes
The Graphics3DControl allows you to position the camera so it looks at the top, front, and other predefined sides of a 3D model.
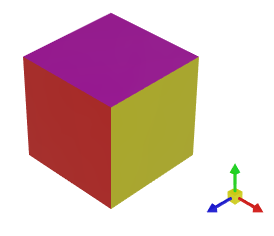
The default scene is IsoXYZ (isometric). In the isometric scene, the X, Y, and Z axes have equal proportions, and the angles between the axes are always 120 degrees:
To change the default scene, use the Camera.DefaultCameraPosition property of a PerspectiveCamera and IsometricCamera objects. You can set Camera.DefaultCameraPosition to the following CameraPosition enumeration values:
Down— The bottom of the model. The camera is positioned along the negative direction of the Y axis.Front— The front of the model. The camera is positioned along the positive direction of the Z axis.IsoXYZ— An isometric scene, in which the X, Y, and Z axes have equal proportions, and the angles between the axes are always 120 degrees.Left— The left side of the model. The camera is positioned along the negative direction of the X axis.Rear— The back of the model. The camera is positioned along the negative direction of the Z axis.Right— The right side of the model. The camera is positioned along the positive direction of the X axis.Up— The top of the model. The camera is positioned along the positive direction of the Y axis.
The following code sets the default camera position to view the right side of a model.
<mx3d:Graphics3DControl.Camera>
<mx3d:PerspectiveCamera DefaultCameraPosition="Right" />
</mx3d:Graphics3DControl.Camera>
At runtime, you can use the following members to view a specific scene of a 3D model:
Graphics3DControl.LookCameraAtScenemethodCamera.Positionproperty of aPerspectiveCameraandIsometricCameraobjects.
g3DControl.LookCameraAtScene(CameraPosition.Left);
Instead of using the LookCameraAtScene method, you can visualize predefined scenes with the Graphics3DControl.LookCameraAtSceneCommand command. Pass a CameraPosition enumeration value as a parameter to this command.
Position the Camera
The PerspectiveCamera and IsometricCamera classes are derived from the base Camera class, which provides members to obtain and adjust the camera's position and orientation in 3D space:
Camera.Positionproperty — The X, Y and Z coordinates of the camera's position.Tip
When you set the
Positionproperty, ensure that the distance between the camera and its target (Camera.Target) is within the allowed range defined byCamera.MinDistanceandCamera.MaxDistance. Otherwise, the model may become hidden.Camera.Targetproperty — The X, Y and Z coordinates of the point the camera is aimed at. The default target is the origin of the coordinate system (0, 0, 0). The target point automatically changes when you pan (shift) the model using theCamera.MoveLeft/Camera.MoveUpmethods, and the keyboard shortcuts and mouse gestures.Camera.UpDirectionproperty — A vector (aVector3value) that specifies the camera's upward direction. For example, whenUpDirectionis set to Vector3(0, 1, 0), the Y axis is pointing up.Camera.LookAtmethod — Sets the camera's target and up direction simultaneously.
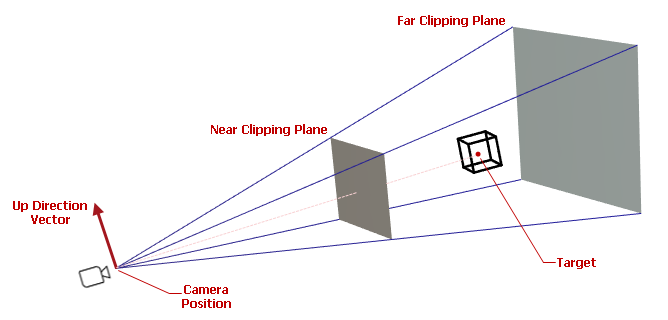
Other camera settings specify the distance constraints and viewing frustum:
Camera.NearClipPlane— The distance between the camera and the near clipping plane. Objects that are nearer this clipping plane are hidden. See alsoFarClipPlane.Camera.FarClipPlane— The distance between the camera and the far clipping plane. Objects beyond the far clipping plane are hidden. Graphics3DControl displays only those objects that are positioned between the near and far clipping planes.Camera.MaxDistance— The maximum allowed distance between the camera (Camera.Position) and the target point (Camera.Target). TheMaxDistanceandMinDistanceproperties specify how far the camera can be away from the target. These properties affect zoom operations performed using theCamera.MoveForwardmethod, and keyboard shortcuts and mouse gestures.Camera.MinDistance— The minimum allowed distance of the camera (Camera.Position) and the target point (Camera.Target).
Example - Place the camera at a custom position
The following code places the camera at the position (X=40, Y=200, Z=40) and sets the Target property to Vector3(0, 0, 0) to point downward at the origin of the coordinate system and view the top of the model. The UpDirection property is set to Vector3(1, 0, 1), aligning the X and Z axes with the left-top and right-top corners of the screen, respectively.
The MaxDistance property is set to 300 ensuring that the new distance between the camera and the target is within the range [MinDistance, MaxDistance].
g3DControl.Camera.MaxDistance = 300;
g3DControl.Camera.Position = new Vector3(40, 200, 40);
g3DControl.Camera.Target = new Vector3(0, 0, 0);
g3DControl.Camera.UpDirection = new Vector3(1, 0, 1);
// or
g3DControl.Camera.MaxDistance = 300;
g3DControl.Camera.Position = new Vector3(40, 200, 40);
g3DControl.Camera.LookAt(new Vector3(0, 0, 0), new Vector3(1, 0, 1));
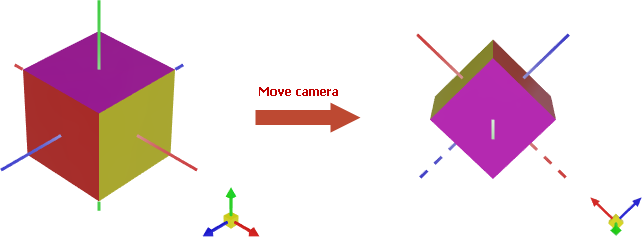
Move and Rotate the Camera
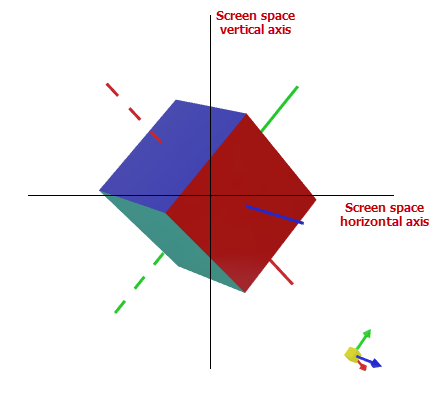
Graphics3DControl supports keyboard shortcuts and mouse gestures that allow users to move (pan), rotate, and zoom the model(s) at runtime. You can also perform these operations in code, using the following methods exposed by the Camera object:
MoveForward— Places the camera closer to (positive offset) or farther from (negative offset) the model.MoveLeft— Shifts the camera to the left (positive offset) or right (negative offset).MoveUp— Shifts the camera up (positive offset) or down (negative offset).Rotate— Rotates the camera around the horizontal and vertical axes of the screen space. The pivot point is the control's coordinate system origin (0, 0, 0).